How the Gallbladder Works: Functions and Importance
How the Gallbladder Works: Functions and Importance
Table of Contents
- Introduction to the Gallbladder
- Anatomy of the Gallbladder
- Functions of the Gallbladder
- Role of Bile in Digestion
- Common Gallbladder Disorders
- Importance of Gallbladder Health
- Conclusion
- References
How the Gallbladder Works: Functions and Importance
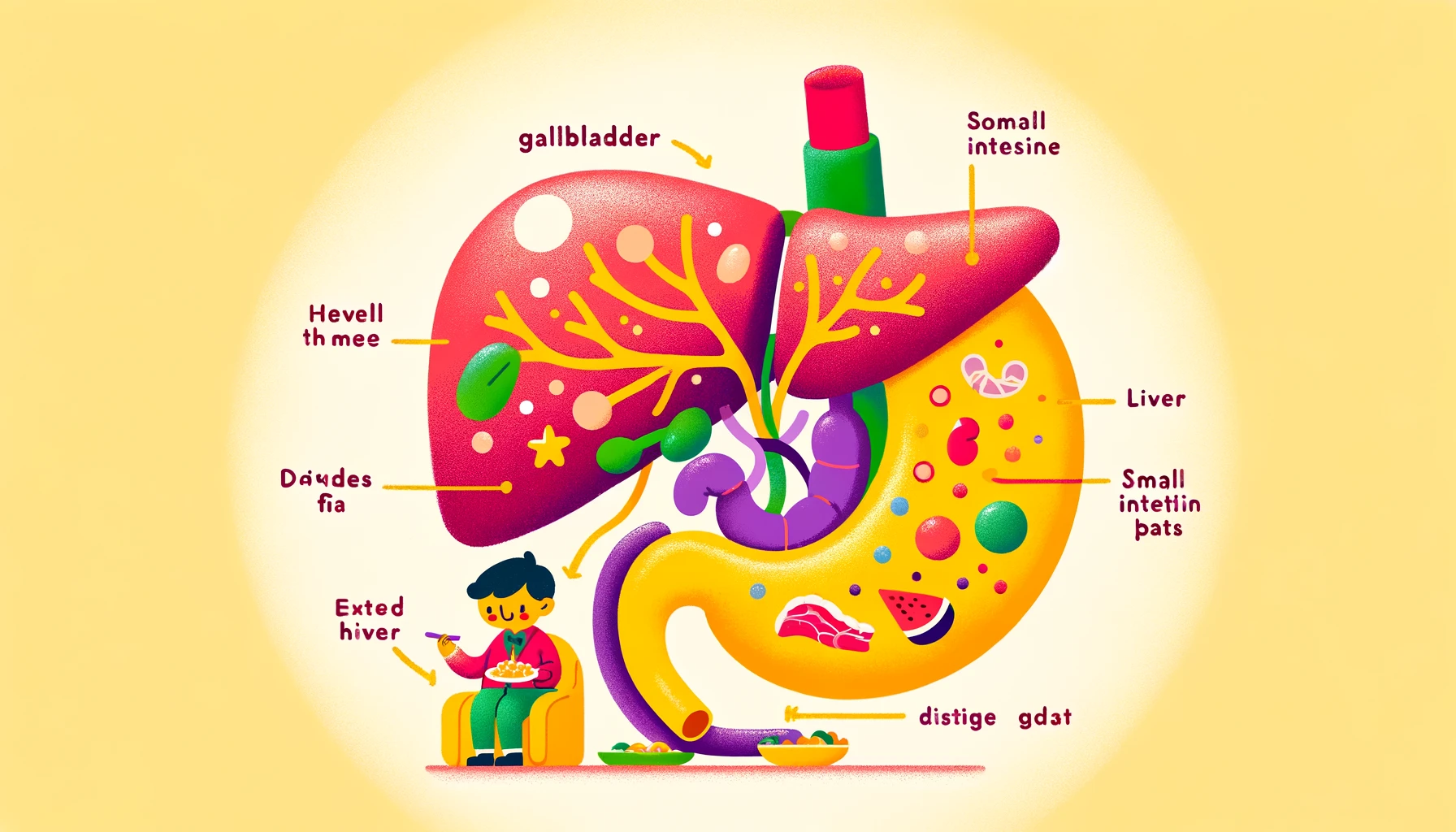
Introduction to the Gallbladder The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver. It plays a crucial role in the digestive system by storing and concentrating bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver. This article explores how the gallbladder works, highlighting its anatomy, functions, and importance in maintaining digestive health.
Anatomy of the Gallbladder The gallbladder is a hollow organ about 3 to 4 inches long and 1 inch wide. It consists of three main parts:
- Fundus: The broad, rounded end that projects beyond the edge of the liver.
- Body: The central portion that lies against the liver.
- Neck: The tapered end that connects to the cystic duct.
The cystic duct joins with the common hepatic duct from the liver to form the common bile duct, which carries bile to the small intestine.
Functions of the Gallbladder The primary functions of the gallbladder are to store, concentrate, and release bile:
- Storage of Bile: The liver continuously produces bile, which is stored in the gallbladder between meals.
- Concentration of Bile: While in the gallbladder, bile is concentrated by the absorption of water and electrolytes, making it more effective in digesting fats.
- Release of Bile: When food, especially fatty food, enters the small intestine, the hormone cholecystokinin (CCK) signals the gallbladder to contract and release bile into the common bile duct, which then flows into the small intestine.
Role of Bile in Digestion Bile plays a crucial role in the digestion and absorption of fats:
- Emulsification of Fats: Bile contains bile salts, which emulsify large fat droplets into smaller ones, increasing the surface area for digestive enzymes to act upon.
- Absorption of Fat-Soluble Vitamins: Bile helps in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) in the small intestine.
- Elimination of Waste Products: Bile also carries waste products, such as bilirubin and excess cholesterol, from the liver to the intestine for excretion.
Common Gallbladder Disorders Several disorders can affect the gallbladder, leading to various symptoms and health issues:
- Gallstones (Cholelithiasis): Solid particles that form in the gallbladder from cholesterol or bilirubin. They can block the bile ducts, causing pain, inflammation, and infection.
- Cholecystitis: Inflammation of the gallbladder, often caused by gallstones blocking the cystic duct. Symptoms include severe pain, fever, and nausea.
- Biliary Dyskinesia: A condition where the gallbladder does not contract properly, leading to poor bile flow and digestive issues.
- Gallbladder Polyps: Small growths on the gallbladder wall, which are usually benign but can sometimes indicate cancer.
Importance of Gallbladder Health Maintaining gallbladder health is essential for proper digestion and overall well-being:
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet low in saturated fats and high in fiber can help prevent gallstones and support gallbladder function.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can reduce the risk of gallstone formation and promote overall digestive health.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps in the proper functioning of the gallbladder and the digestion process.
- Monitoring Symptoms: Being aware of symptoms like abdominal pain, nausea, and jaundice can help in early detection and treatment of gallbladder disorders.
Conclusion Understanding how the gallbladder works and its role in digestion is crucial for maintaining digestive health. The gallbladder’s functions in storing, concentrating, and releasing bile are vital for the efficient digestion of fats and the absorption of essential nutrients. Taking steps to maintain gallbladder health through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and hydration can prevent common gallbladder disorders and ensure proper digestive function.
<ⓒ WizardMedics (wizardmedics.com)>